Surface water migrates into the groundwater by infiltration through the soil, or by runoff into areas where the water table is above the surface of the ground. Carried by the surface water, pollutants such as agricultural pesticides and fertilizers, oils and salts from roadways, and industrial effluents can make their way into the groundwater.
Use MAGNET to model the impact of a contaminated stream on a nearby drinking water well based on the following parameters (see figure) ... and perform a sensitivity analysis with respect to different ways of representing polluted stream
- prescribed recharge, with a specified stream water concentration
- prescribed head, with a specified stream water concentration
- two way head dependent flux, with a specified stream water concentration
Numerically experiment with the effect of stream leakage coefficient (or leakance) characterizing stream-aquifer connection.
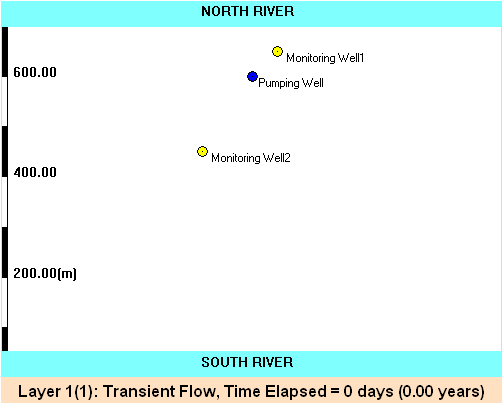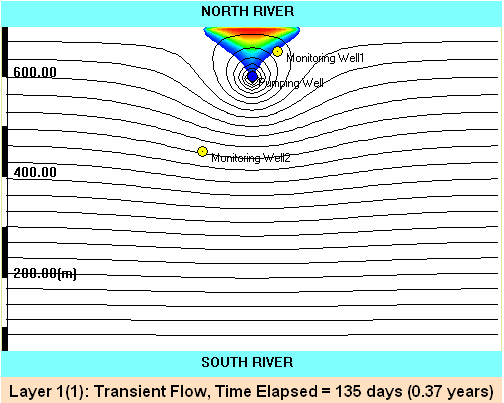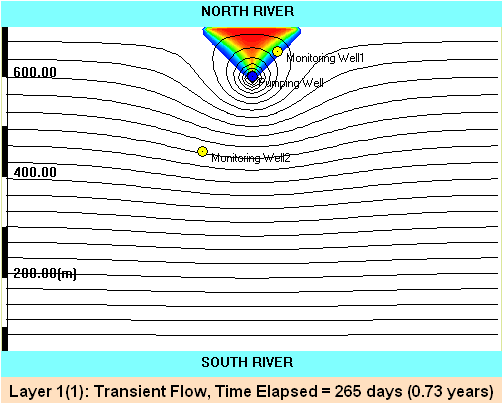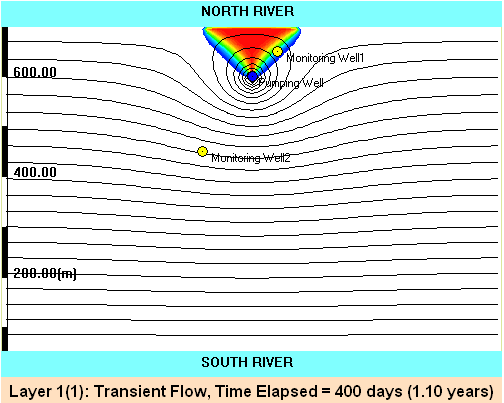
Video: Migration of contaminated stream water toward a nearby drinking water well . Model parameters: Q = 500 GPM; Hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer: 100
ft/day; Aquifer thickness: 100 ft; Effective porosity: 0.2; River stage difference: 25 ft
MAGNET/Modeling Hints:
- Use ‘Synthetic mode’ in MAGNET to create a model domain.
- You may follow the model set-up described in the animation caption above.
- Use line and features as prescribed head boundaries to generate the head difference from the south edge to the north edge of the model.